Global research: 3 out of 4 professionals do not feel ready to work in a digital-first world
Global Digital Skills Index research from Salesforce revealed a growing global digital skills crisis and the urgent need for action. The Index is based on over 23,000 workers in 19 countries reporting their readiness to acquire the key digital skills needed by businesses today and over the next five years. The Index follows a Salesforce-commissioned study by leading research institute RAND Europe to examine the evidence associated with various aspects of the digital skills gap.
What is the digital skills gap? According to the research, the digital skills gap means there are not enough people with the right digital skills to power companies' digital transformation now and in the future.
There is a low supply and high demand for digital skills, and the gap continues to widen due to factors like:
- Tech talent is outpacing an already short supply (in fact, 54% of American workers believe technology will advance faster than workforce skills)
- Emerging technologies that amplify the need for digital skills
- High costs and disorganized approaches to traditional education that increase barriers to learning
- Access to digital infrastructure and skills limited by socio-economic status
What is the cost associated with the digital skills gap? Research from Salesforce and RAND Europe shows that the digital skills gap is disruptive to business growth, citing that 14 of the G20 Countries could miss out on $11.5 trillion in cumulative GDP growth.

Businesses must invest in improving the digital skills gaps that exist by investing in employee, customer and business partner training programs.
Shutterstock
What are digital skills?
Digital skills are broadly defined as the skills needed to “use digital devices, communication applications, and networks to access and manage information,” from basic online searching and emailing to specialist programming and development. These skills help people communicate and collaborate, develop and share digital content, and problem-solve in a work-anywhere world.
What are examples of digital skills?
Entry-level digital skills can include:
- Computer literacy
- Data entry
- Social media
- Web-based communications and research
- Word processing
- Email and chat
- Secure information processing
Advanced digital skills can include:
- Programming, web, and app development
- Digital business analysis
- Digital marketing and content creation
- Digital design and data visualization
- Digital product management
- Data science
- User experience design
Top priorities for HR leaders in 2022:
1 building critical skills and competencies
2 organizational design and change management
3 current and future leadership bench pic.twitter.com/EOmEdxTyWd
— Vala Afshar (@ValaAfshar) January 10, 2022
According to the skills index, nearly three-quarters of respondents (73%) do not feel equipped to learn the digital skills needed by businesses now and even more (76%) do not feel equipped for the future. The research also shows that there is a major gap emerging between everyday digital skills and those needed for work, especially among younger workers. In addition, the use of collaboration technologies is viewed as the most important digital workplace skill for workers over the next five years.
Here are the key takeaways of the global digital skills index survey findings:

82% of global workers plan to learn new skills to grow their career.
Salesforce
The global digital skills gap
- The social media skills gap: 83% have ‘Advanced' or ‘Intermediate' everyday social media skills. However, only one-third feel prepared for the workplace digital skills needed over the next five years. Over 60% of global respondents say skills in collaboration technology like Slack are viewed as the most important skills needed by businesses today and over the next five years. Only 25% rated themselves ‘Advanced' in those collaboration technology skills needed specifically for the workplace. Everyday skills such as social media and web navigation don't necessarily translate to the core workplace digital skills businesses need to drive recovery, resilience and growth. More than two-thirds of all Gen Z respondents (64%) say they have ‘Advanced' social media skills — supporting the stereotype of digital mastery among the younger generation — but less than a third (31%) believe they have the ‘advanced' digital workplace skills needed by businesses now.
- The generational skills gap: Only 31% of Gen Z respondents, the first digitally native generation, feel ‘very equipped' for a digital-first job right now. Currently, not many Gen Z respondents believe they have ‘Advanced' digital skills in areas like Coding (20%), Data Encryption & Cybersecurity (18%), and AI (7%). Just 17% of Baby Boomers believe they are ‘very equipped now' for digital-first employment.
- The leadership and workforce skills gap: A disconnect also remains between senior leadership and their workforces in terms of participation in digital education and expectations of digital readiness for the near future. A majority of senior leadership respondents (57%) said they are prepared with the digital skills necessary over the next five years. This contrasts with just 37% of managers.
This gap is a concern — but it also presents an opportunity. With companies around the world rapidly transitioning to digital-first models, the demand for employees with digital skills has soared. While the research highlights that certain countries feel more digitally ready than others, it is clear that all nations still have a lot of work to do. Bridging the digital divide is imperative to maintaining and improving living standards across the globe. Only 17% of all respondents consider themselves ‘Advanced' in workplace digital skills, while nearly half (49%) still rate themselves as ‘Beginner'.
Businesses, governments and communities can work together in closing the digital skills gap by harnessing existing learning communities, investing in young generations and promoting training programs focused on top digital skills.
The survey revealed remaining skill gaps in some of these critical areas:
- Collaboration Technology Skills has the biggest percentage of ‘Advanced' practitioners. This still only equates to roughly 25% of survey respondents.
- Despite 58% saying Encryption & Cybersecurity Skills are particularly important, only 14% report Advanced knowledge of the subject.
- Nearly half of all respondents view digital sustainability skills as important ‘now and in the next five years'. As little as 13% of all respondents, and just 16% of business owners, have ‘Advanced' digital skills for operating technology that promotes sustainable business activities like tracing, measuring and analyzing climate data within an organization.

3 out of 4 global workers do not feel ready to succeed in the digital economy due to low digital skills proficiencies.
There's a big gap between digital skills training for leadership and lower-level employees.
-
57% of senior leadership respondents believe they will be ready with the workplace digital skills needed over the next five years. This contrasts with just 37% of managers and only 34% of those self-employed.
-
60% of senior leadership respondents are actively participating in digital learning and training initiatives now, compared to 34% of managers and 23% of employed contractors.
You can access an interactive Tableau dashboard that displays the data.
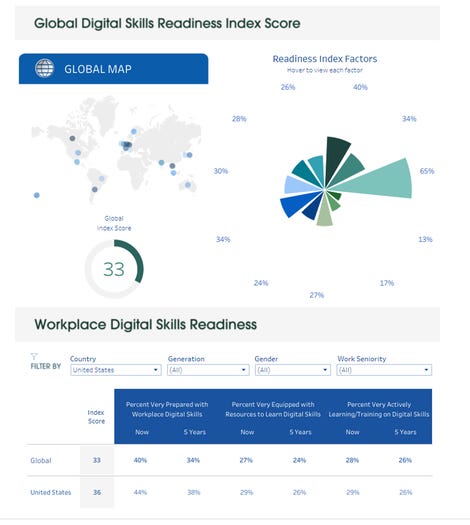
2022 Global Skills Index Interactive Tableau Dashboards
TableauThe most important digital skills needed by businesses today
According to the Digital Skills Index, skills in collaboration technology like Slack are viewed as the most important skills needed by businesses today and over the next five years — 63% of global respondents say this. But despite respondents' prowess with everyday collaboration technology like social media, only 25% rated themselves ‘Advanced' in those collaboration technology skills needed specifically for the workplace.
According to respondents, the five most important digital skills businesses need to invest in are:
- Collaboration Technology Skills: synchronous/asynchronous collaboration platforms
- Digital Administrative Skills: digitally filing paperwork, presenting important information virtually, developing digital-first processes
- Encryption & Cybersecurity Skills: skills to help protect data from unauthorized parties
- E-Commerce & Digital Trade Skills: sales order management and payments, to shipping and fulfillment services
- Project Management Technology Skills: managing project timelines, people, and processes with project management software
Businesses have a critical role to play
Over half of the Index respondents (51%) want to learn new skills to help them grow their careers. By harnessing the potential of existing workforces, businesses can speed progress towards closing their skills gaps. The Index also reveals that younger respondents have greater confidence and ambition to learn new skills — over one-third are ‘very actively' learning and training for skills needed over the next five years compared to 12% of Baby Boomers. Businesses have a major opportunity to nurture young talent by providing tailored and continuous learning opportunities that will help drive growth and innovation, increase equity and engagement and create strong leaders for the future.
Now, more than ever, businesses are responsible for creating a close collaboration with governments, partners, and communities to tackle the widening skills crisis. Collaboration is key to ensuring the right kinds of training and recruitment opportunities scale up to match digital demand and equally reach all aspects of society.
Top 10 technology trends that will shape the coming decade:
1 automation RPA
2 5G and IoT
3 cloud and edge compute
4 quantum computing
5 applied AI (ML NLP)
6 software 2.0
7 trust architecture (blockchain)
8 bio revolution
9 NG materials
10 clean tech https://t.co/Byp46APNHI pic.twitter.com/nGmltWpjfp— Vala Afshar (@ValaAfshar) January 24, 2022
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, it is clear that as technology evolves, so do digital skills. Technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), distributed ledgers (Blockchain), extended reality (augmented reality AR, virtual reality VR, and interactive 3D), cloud computing, and internet of things (IoT)/sensor technologies are pervasive in all companies across all sectors. The increase in business requirements for digital skills by up to 50% in Europe and the United States.
BIG IDEAS 2022:
1 AI
2 Digital Consumer
3 Digital Wallets
4 Public Blockchains
5 Bitcoin
6 Ethereum DeFi
7 Web3
8 Gene Editing
9 Multi-Omics
10 Electric Vehicles
11 Autonomous Ride-Hail
12 Autonomous Logistics
13 Printing and Robotics
14 Orbital Aerospace https://t.co/whkDbaq4wV pic.twitter.com/LgWoIiZAkx— Vala Afshar (@ValaAfshar) January 26, 2022
One effective method of reducing the digital skills gap is with micro-degrees or focused online degrees in a specific area of study. Instead of adding to the $1.7 trillion currently owed in student debt, working professionals can quickly earn more focused degrees that can lead to new jobs in specified fields, like IT. Trailhead, for example, is Salesforce's free online learning platform that helps anyone skill up for jobs in the Salesforce ecosystem.
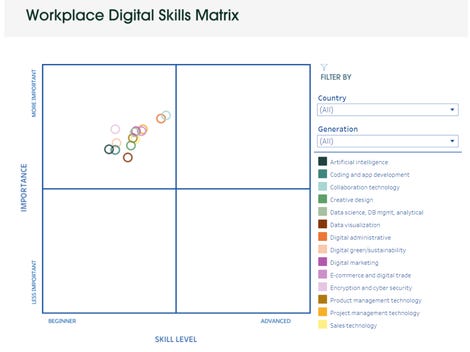
The interactive Tableau dashboard shows that globally, workers show beginner level understanding and acquired skills for new emerging digital technologies.
TableauValues create value. Businesses that value education, trust and stakeholder success based on transferable and relevant skills development are well positioned to co-create real societal value. Business is the greatest platform for change, if and only if all stakeholders — employees, customers, partners and communities — are continuously gaining and sharing new knowledge with a purpose of personal and economic prosperity.
We need to rethink our approach towards education and training programs urgently. The education and re-skilling of our stakeholders must be affordable, easily accessible, relevant and delivered in a timely and flexible manner. It is only through sustained investment and active partnerships businesses can build a platform for change.

